In the not-so-distant future of 2025, the world of cybersecurity is at a crossroads. With a projected surge to a staggering $10.5 trillion in cybercrime costs, it’s clear that our digital fortresses are facing unprecedented challenges. This astronomical figure serves as a stark reminder that the audacity and complexity of cyberattacks are reaching new heights.
In the age of digital connectivity, the internet has seamlessly woven itself into the fabric of our daily lives. It’s a bustling realm where 197.6 million emails are exchanged, 1.6 million dollars are spent online, and almost 415,000 apps are downloaded every minute. This dynamic environment brings us unparalleled communication, learning, and technological possibilities. However, amidst this digital expanse, we find ourselves exposed to a myriad of web-based threats that can compromise our security.
But in the face of this evolving threat, there’s no room for a passive defense. We need to shift gears towards a proactive and multifaceted approach to cybersecurity. It’s not just about keeping an eye out; it’s about anticipating and neutralizing threats before they strike. This demands the integration of cutting-edge technologies and the fostering of collaboration across sectors, creating a united front against the ever-shifting tactics of cyber adversaries.
Let’s dive into the world of web security and explore the numbers that define the challenges we face.
How many people get hacked every year?
Unfortunately, there’s no single, precise answer to how many people get hacked each year. It’s a complex issue with several factors clouding the numbers:
Underreporting: Many hacking incidents go unreported for various reasons, like fear of judgment, lack of awareness, or the difficulty of proving an attack occurred. This significantly underestimates the true number of victims.
Studies indicate anywhere from 71 million to 800,000+ people are affected by cyberattacks annually.
Reports suggest a cyberattack occurs roughly every 39 seconds, potentially impacting hundreds of thousands of victims daily.

Remote work challenges
Increased Risks:
- More attack points are due to personal devices, networks, and unsecured Wi-Fi.
- Phishing and social engineering scams make it easier to target isolated workers.
- Weaker endpoint security on personal devices compared to company equipment.
- Unsecured public Wi-Fi networks create vulnerabilities.
- Blurred lines between personal and professional data make exploitation easier.
Causes of network security vulnerabilities
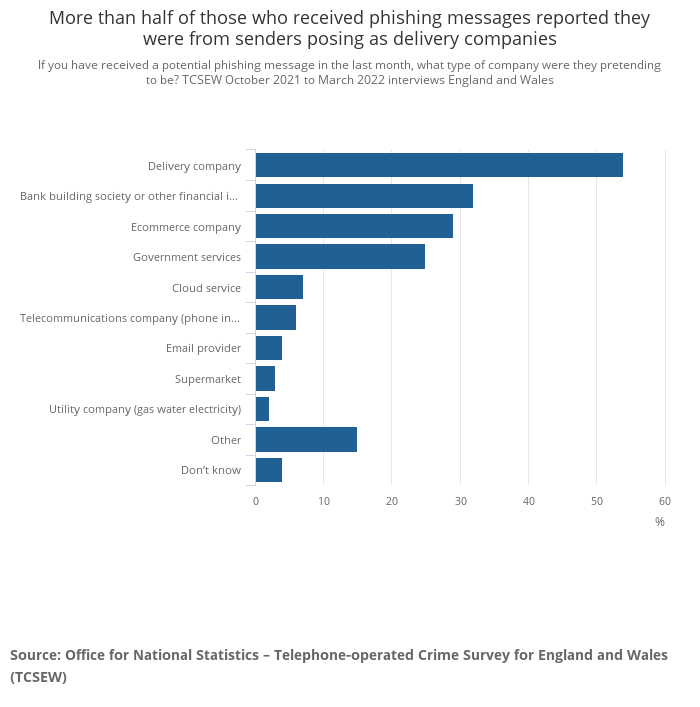
Phishing attacks
Frequency:
- Hackers breach an average of 30,000 websites daily.
- 81% of organizations have experienced an increase in phishing attacks since March 2020.
- A record number of phishing attacks were observed in Q3 2022.
Impact:
- 323,972 internet users fell victim to phishing in 2021, representing half of all cybercrime victims.
- 83% of data breaches involve a human element, often including phishing and stolen credentials.
- Phishing is the most prevalent cyber threat in the US.
- The average individual loses $136 per phishing attack, totaling $44.2 million stolen in 2021.
- 83% of UK businesses suffering cyberattacks in 2022 reported phishing as the attack type.
Ransomware Attack
Is malware holding your files hostage for money? That’s ransomware, and it’s become a super common problem, happening like every 11 seconds! Security experts guess that there were over 700 million attempts in 2021 alone, targeting both people and businesses. Yikes!
Impact:
- 34% of ransomware attacks resulted in ransom payments in Q2 2023.
- 20% of all cybercrimes in 2022 were attributed to ransomware.
- Ransomware costs are expected to reach a staggering $265 billion annually by 2031.
- 20% of ransomware costs stem from reputation damage, not just the ransom itself.
- 623.3 million attacks were launched in 2021, and numbers keep rising.
Malware attacks
Malware, the malicious software designed to wreak havoc on your devices, lurks around every digital corner. From annoying pop-ups to data-stealing Trojans, the types and impacts of malware attacks are varied and ever-evolving
- In 2021 alone, there were an estimated 5.4 billion malware infections globally, translating to roughly 15 attacks per second.
- Mobile devices are increasingly targeted: Kaspersky reports that in 2021, malicious applications were detected on nearly 1 in 4 Android devices.
- Over 70% of all system intrusion breaches involve malware.
IoT and DDoS attacks
The rising number of connected devices in the Internet of Things (IoT) poses a significant threat as they become targets for attackers launching Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks. Here are some key statistics highlighting the problem:
Prevalence:
- Over 112 million IoT cyber attacks occurred globally in 2022, a massive 87% increase from 2018.
- DDoS attacks involving IoT devices increased from 11% in 2018 to 52% in 2019.
- A single botnet of compromised IoT devices launched a 15 Tbps DDoS attack, the largest on record, in 2016.
Impact:
- The average cost of a DDoS attack is $4.45 million globally, with attacks using IoT devices potentially causing even greater damage.
- Healthcare, finance, and media industries are frequently targeted by DDoS attacks involving IoT devices.
- Disruptions caused by DDoS attacks can negatively impact critical infrastructure, leading to widespread service outages and economic losses.
Who is a potential victim?
Unfortunately, anyone connected to the internet is a potential victim of a cyberattack. The vast and interconnected nature of the online world makes it difficult to pinpoint specific groups as more or less susceptible. However, certain factors might increase an individual’s or organization’s risk:
Individuals:
- Less technical knowledge: Users with a limited understanding of cybersecurity practices might be more vulnerable to phishing scams, social engineering attacks, or malware through unsafe downloads.
- Reliance on personal devices: Using personal devices for work or storing sensitive information without proper security measures can create entry points for attackers.
- Neglecting software updates: Failing to update operating systems and applications leaves devices vulnerable to known vulnerabilities exploited by attackers.
- Weak passwords: Reusing passwords or using easily guessable ones makes unauthorized access easier for attackers.
Organizations:
- Large attack surface: Organizations with extensive networks, including various devices and user accounts, offer more points of vulnerability for attackers to exploit.
- Storing sensitive data: Businesses handling sensitive customer information like financial data or personal records become prime targets for attackers seeking financial gain or identity theft.
- Remote workforces: The shift to remote work introduces new challenges, like securing personal devices used for work and managing access to sensitive data remotely.
- Limited cybersecurity resources: Smaller organizations might lack the budget or expertise to implement robust cybersecurity measures, leaving them vulnerable.
Causes of Data Breach
While physical security vulnerabilities are present, the most common causes of data breaches in cybersecurity typically originate from other sources. Here’s a breakdown of the major culprits:
Top Causes:
- Weak Credentials: Stolen or weak passwords are the easiest entry point for attackers.
- Application Vulnerabilities: Unpatched software with known weaknesses provides hackers with exploitable holes in your defenses. (Source: Zluri)
- Malware: Malicious software like viruses, ransomware, and spyware can steal data, encrypt it for ransom, or disrupt operations.
- Social Engineering: Phishing emails, fake websites, and other deceptive tactics can trick users into giving up sensitive information.
- Insider Threats: Malicious insiders or accidental errors by employees can lead to data exposure.
Other Common Causes:
- Misconfigured Systems: Improper setup or lack of security protocols can create vulnerabilities.
- Lost or Stolen Devices: Unsecured devices containing sensitive data can be compromised.
- Physical Security Lapses: Lack of access control or surveillance can enable physical theft of data.
- Supply Chain Attacks: Vulnerabilities in third-party vendors can be exploited to access your data.
Data breach stats
Data breaches are a constant threat in today’s digital world, and unfortunately, the statistics paint a concerning picture:
Frequency:
- Global: Over 8 million records were exposed in Q4 2023 alone, and the number is steadily increasing.
- US: In 2022, there were 1,802 data breaches, exposing 422 million records.
Financial Impact:
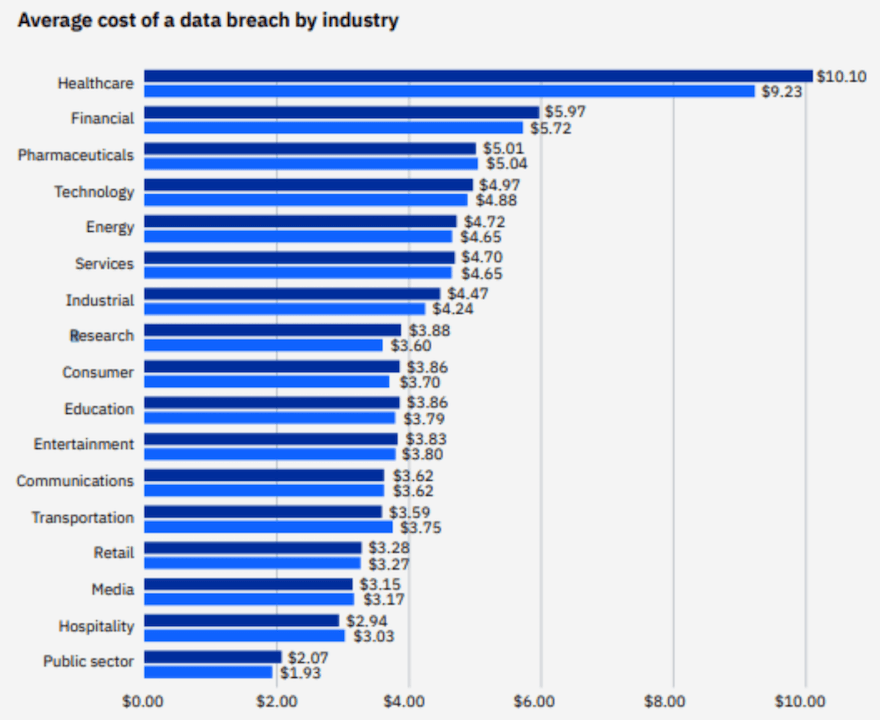
- Global: The average cost of a data breach is $4.45 million, with the US seeing the highest average at $9.48 million.
- Leaked Record: Each lost record costs an average of $165.
Causes:
- Human Error: 95% of breaches are attributed to human error, including weak passwords and phishing scams.
- Financial Gain: 93% of breaches are motivated by financial gain, like stealing credit card information.
- Cloud Storage: 45% of breaches involve cloud-based data.
Other concerning statistics:
- Small Businesses: 46% of breaches target companies with fewer than 1,000 employees.
- Critical Infrastructure: 79% of critical infrastructure organizations lack secure architecture.
- Healthcare: 30% of large breaches happen in hospitals.
Cost of Cybersecurity
Organization size and industry: Larger organizations and those in highly regulated industries generally spend more on cybersecurity. Security posture: Organizations with existing vulnerabilities or a history of breaches might need to invest more heavily to improve their defenses. Specific threats: Addressing specific threats like advanced persistent threats (APTs) requires specialized tools and expertise, increasing costs. Security solutions chosen: On-premise solutions can be expensive to maintain, while cloud-based solutions may have recurring subscription fees.
Here’s a breakdown of some key cost elements:
IT Budget Allocation:
- Average: Companies typically allocate around 10% of their IT budget to cybersecurity.
- Small Businesses: Average spending per employee is around $2,700 annually.
- Global Market: Expected to reach $1.52 trillion by 2025.
Specific Components:
- Software tools: Firewalls, anti-malware, vulnerability scanners, etc. (Variable costs)
- Hardware: Secure servers, network equipment, etc. (Variable costs)
- Personnel: Security analysts, incident responders, training staff, etc. (Salary + benefits)
- Training and Awareness: Employee education on security best practices. (Variable costs)
- Cybersecurity insurance: Can help mitigate financial losses from breaches. (Premium costs)
Historic Data Breaches
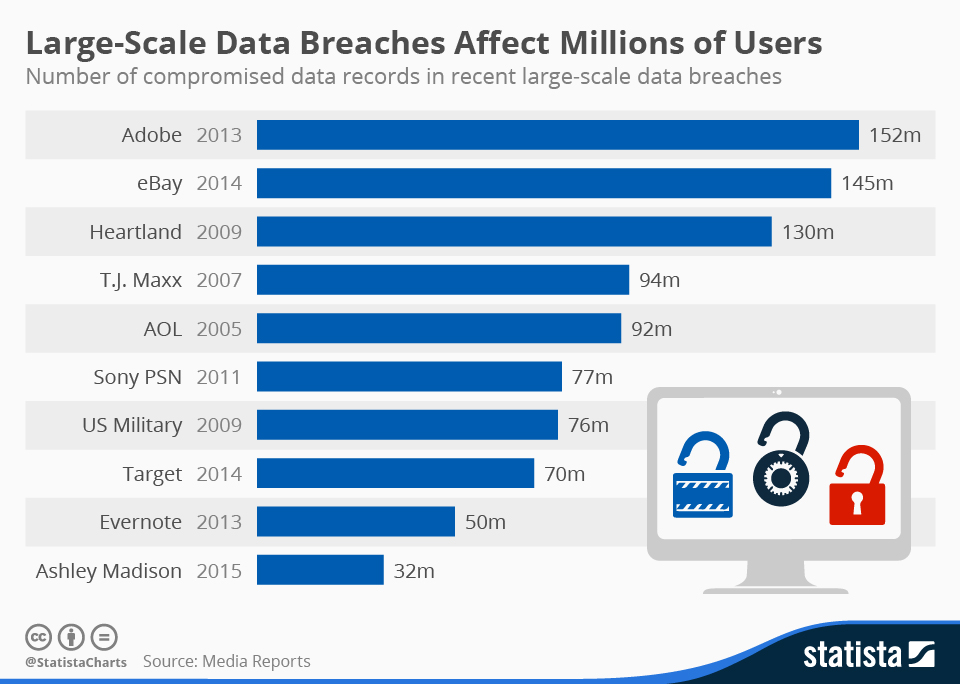
Yahoo (2013-2014):
Impact: 3 billion user accounts were compromised.
Data: Usernames, email addresses, hashed passwords, and, in some cases, encrypted or unencrypted security questions and answers.
Equifax (2017):
Impact: The personal information of 147 million people was exposed.
Data: Social Security numbers, birth dates, addresses, and in some cases, driver’s license numbers.
Marriott International (2014-2018):
Impact: Approximately 500 million guests were affected.
Data: Names, mailing addresses, phone numbers, email addresses, passport numbers, and encrypted payment card information.
Capital One (2019):
Impact: The personal information of over 100 million individuals was compromised.
Data: Names, addresses, credit scores, social security numbers, and bank account numbers.
Facebook-Cambridge Analytica (2018):
Impact: Up to 87 million Facebook users were affected.
Data: Users’ personal information obtained without explicit consent, including likes, location data, and other profile details.
LinkedIn (2012):
Impact: Around 167 million accounts were compromised.
Data: Passwords hashed and stored in unsalted form.
Adobe (2013):
Impact: The data of 38 million users was exposed.
Data: encrypted passwords and password hints.
eBay (2014):
Impact: The personal information of 145 million users was compromised.
Data: names, addresses, dates of birth, and encrypted passwords.
Uber (2016):
Impact: Data of 57 million users and 600,000 drivers were compromised.
Data: Names, email addresses, phone numbers, and driver’s license numbers.
Target (2013):
Impact: Credit and debit card information of 40 million customers is exposed.
Data: Card numbers, expiration dates, and CVVs.
Source: FBI, Verizon, APWG, Statista, Comparitech, A10 networks, IBM, Cloudflare, Zluri, Kaspersky, Lepide, and Terranova Security
Hello, I'm Harshi Gupta, a seasoned penetration tester with expertise in both internal and external assessments. Cybersecurity is not just a career path for me; it's my hobby and passion. With a wealth of experience in identifying and mitigating security vulnerabilities, I am dedicated to ensuring the resilience of organizations' digital assets. For networking opportunities and engaging discussions, feel free to reach out to me via LinkedIn and Twitter.
